introduction As a module for access authentication and identity authentication, a smart card is one of the necessary devices for a user terminal in a mobile communication network. In M2M (Machineto Machine), the smart card also continues this role, storing user identity data and access information for legitimate users to access the carrier network. To some extent, since M2M uses objects as the main body of network connections, M2M's terminal types are richer and more complex than mature personal terminals. Therefore, identification and authentication of their identity is more important. Smart cards are used as identity. The identification module, its status and role should also be further strengthened. The smart card applied to the M2M can be referred to as the M2M card. In the M2M three-layer architecture, the terminal and the sensing layer realize the information collection through the perception of the object; the network layer completes the information transmission and partial processing through the network connection; the application layer Provide users with an application. The M2M card, as part of the terminal and sensing layer, has many functions. 1) Provide identity authentication. As the user equipment identity authentication module, the user equipment accesses the identity of the mobile network and performs authentication, and completes the network authentication security authentication. 2) Provide application support. Load some user equipment applications to meet the business requirements of M2M data collection, parameter measurement, service monitoring, positioning and command scheduling. 3) Security mechanism guarantee. The smart card security guarantee capability provides security mechanisms for user network access, service access, data transmission, and information storage. 1 M2M impact on smart cards M2M's special application scenarios and complex application environments put new demands on smart cards. After years of research and development, these requirements have gradually become clear and defined in international and domestic standards. Since the M2M card is usually implemented based on the UICC platform and is called M2MUICC in the standard, its requirements can be summarized as follows. 1) Package shape. M2M UICC requires a more diverse package shape. For many industries, the traditional plug-in UICC card card separation form is difficult to meet its special requirements, requiring a unique package form, namely MFF (M2M Form Factor). The MFF UICC is soldered together with the communication module, and has a smaller specification size, which can realize a tight and firm physical connection and reliable communication between the UICC card and the terminal, and is a type of embedded UICC card. This UICC card usually adopts the SMD chip packaging process and has all the functions of the traditional UICC card, but its package shape is obviously improved in terms of anti-vibration and anti-theft. 2) Hardware features. The hardware characteristics of M2M UICC need to meet the industrial requirements of M2M. It is different from the unified environment requirements of ordinary UICC cards. The environment requirements of M2M UICC are usually divided into several levels. For example, for the operating temperature requirements, the normal UICC card is -25 ° C ~ +85 ° C, and M2M UICC has four levels of operating temperature requirements, respectively TS (-25 ° C ~ +85 ° C), TA (-40 ° C ~+85°C), TB (-40°C~+105°C), TC(-25°C~+125°C), M2M cards used under different conditions in different industries can have different levels of requirements. In addition to temperature, there are other requirements, such as anti-vibration requirements in the automotive industry, longer data retention time requirements in the power industry, and more data read and write times in data collection services. These are typical M2M special for UICC cards. The hardware feature requirements require a higher level of requirements. 3) Management mode. After years of development, the distribution management of telecom smart cards has formed a relatively stable process and mode, that is, the operator provides user data, and the card manufacturer manufactures the specified card products according to the data and supplies them to the operators, and then the operators provide the finished products. The card is given to the end user, and the operator dominates the release management process. Some features of M2M and M2MUICC put forward new requirements for this model. This is mainly for two reasons. First, in M2M, industry customers or M2M service providers appear as new roles between operators, card manufacturers and end users, which may lead to problems such as the possibility of facing M2MUICC. Second issue and transfer of operator contract relationship; Second, the introduction of embedded UICC (eUICC), the convenience of data update after release is reduced, and the data management mode needs to be changed; therefore, M2M UICC and its represented operators sign up Relationships are no longer simple linear relationships. They begin to generate more complex states and processes such as change, transfer, recycling, and redistribution. Remote management of data gradually becomes a requirement, and management objects also draw code number data from the initial air-based service. Gradually expand and even involve all configuration data. 2 M2M card standardization ETSI SCP is a technical committee specializing in smart card research. The committee released the ETSI TS 102.671 standard [1] in April 2010 (the latest version was released in September 2011), which defines the physical and logical characteristics of M2MUICC, including the following Aspect of the content. 1) Environmental level definition of M2M UICC. It defines nine environmental indicators such as working and storage temperature, humidity/reflow, humidity, corrosion, vibration, contact corrosion, impact, data retention time and minimum update times. Each environmental indicator is divided into several levels. 2) Physical characteristics of the M2M UICC. M2M UICC can be one of the two forms of traditional form Plug-in and unique form MFF, and mainly defines the physical size, contact position and other requirements of MFF, including MFF1 and MFF2. 3) Electrical and logical characteristics of the M2M UICC. In addition to the individual requirements of the supply voltage, it basically follows the requirements of the ordinary UICC. 4) Device matching mechanism of M2M UICC. The M2M terminal is required to support both the secure channel and the CAT application of the UICC. In addition, the SCP also released the ETSI TS 103.383 standard for eUICC [2] this year, which defines the remote management requirements of eUICC used by M2M, mainly for summary requirements, including the following aspects. 1) Define a series of application scenarios for eUICC remote management. Including eUICC batch configuration, new networked device first configuration subscription data, contract data replacement and SM-SR replacement. 2) According to the above scenario, define the requirements of eUICC that supports remote management. Including basic requirements, such as compliance with basic requirements, unique and unchangeable identification, capacity set, application, file structure, such as configuration capability set and operational capability set, composition of capability set, etc. Aspects, such as the creation and installation process of the capability set container, the download, installation, deletion, activation, deactivation process of the capability set, etc.; in terms of security, if there is a security mechanism to ensure the authorization, authentication, integrity and confidentiality of the capability set management Sex. The above two standards are standards currently set by ETSI specifically for M2MUICC. Other standards organizations have also conducted research on M2M UICC. Among them, GSMA has set up a special task force to study eUICC remote management technology. Since 2011, it has successively formulated white papers for embedded SIM requirements and application scenarios [3], eUICC remote configuration architecture. [4] and other technical advice. 3GPP officially started M2M research in the R10 phase, and related to M2MUICC is mainly the research report on the security requirements of remote configuration and contract relationship conversion of TR 33.812 M2M equipment [5]. 3 M2M card development problem analysis At present, the work on M2M cards is mainly concentrated on the above aspects. After examining the attributes and functions of each requirement, the main purpose of the package shape and hardware characteristics is to meet the basic needs of M2M cards in special industries and special environments, and to ensure M2M cards. The availability and durability are basically realized in the production and production process, and the promotion of M2M card development is limited; the demand for distribution management is the expansion and improvement of the existing management mode, which belongs to the support technical requirements, although the support for air card is improved. The ease of use of M2M cards, but it is still difficult to open up new application scenarios. In contrast, the development of M2M card business capabilities is relatively weak, whether it is technical research or application practice, there is relatively little progress in this area. The M2M service function has diverse requirements and is closely related to the specific application scenarios of the M2M card. It can be said that there are many uncertainties, which increases the difficulty of developing the M2M card service, so it is difficult to see the suitable M2M card service at present. It should be noted that if the M2M card cannot carry more business functions, its positioning in M2M may be limited to the basic requirements, and the role may be gradually reduced, and in fact this sign has already been shown. In the current practical application of M2M, due to the simple business requirements, the M2M card has less functional requirements, and only needs basic authentication capabilities, even in the (U)SIM card in the personal terminal, OTA, STK/ has already become popular. Features such as USAT are not required, and it is the simplest category in the telecom smart card product line. The M2M card seems to show a trend of returning to basic authentication. If this trend continues, the development momentum of the M2M card will be severely constrained, affecting its development prospects in M2M. Therefore, it is necessary to develop the M2M card business function and explore the M2M card service that truly meets the needs of users and has a good application effect. 4 short-range wireless communication M2M card technology solution In addition to the usual contact cards, contactless cards are also closely related to M2M. The use of contactless cards is very common, such as access control, ticketing, identity tags, payment, etc. In recent years, the development trend of the combination of contactless cards and telecom smart cards such as (U)SIM has also received wide attention. The mobile payment, school-enterprise card and other services that have been promoted are considered to be hot spots in the mobile service. Although the application scenarios and presentation forms are different, and the implementation schemes are different, the short-range wireless communication technology is used to exchange information with other non-contact communication devices (such as card readers) through smart cards with non-contact communication capabilities. . In fact, with the development of short-range wireless communication technology and smart card technology, the combination of the two can also be derived from other types of applications. In particular, M2M aims to realize the interconnection between objects, and the characteristics of information collection and information transmission can excite another function of smart cards, which is to organize local wireless networks through wireless communication technologies to make smart cards. In addition to remote communication through the mobile network, it also undertakes the local communication function, and expands into a service node with two communication capabilities combined with two communication methods. Different from the one-to-one application mode of ordinary contactless card services such as access control and payment, the service needs to support one-to-many and many-to-many application modes, and each communication node forms a certain structure and communicates with each other. Although the current business is still under discussion and development, it has a close relationship with M2M and may have a relatively large development potential. The smart card for short-range wireless communication applied to M2M may be named as short-distance communication M2M card, which refers to the integration of wireless function module with short-range communication capability in M2M card, which can be used together with M2M communication terminal to support ordinary telecommunications. In addition to the smart card (U)SIM application, wireless communication functions are implemented. The short-range communication M2M card embeds the functional entities such as the security control chip, memory, wireless chip and antenna into the M2M card to realize both contact and non-contact communication functions. It mainly includes two modules, wherein the (U)SIM card module supports normal mobile communication authentication, and the wireless function module supports user terminal equipment and peripheral devices (wireless communication nodes) to interact, and can realize point-to-point communication and networking communication. The built-in micro operating system provides secure management of various information within the card. Figure 1 is a hierarchical logical architecture of such a card. Figure 1 Layered logical architecture of short-range communication M2M card Short-range communication M2M cards can use IEEE 802.15.4 LRWPAN/Zigbee technology. The technology is one of the wireless communication technologies that can be implemented based on smart cards, and has a certain application basis, and compared with other smart card-based technologies such as RFID and NFC, the technology has low cost, low power consumption, and good at networking applications, and can U) SIM card combination and no terminal modification, the implementation is less difficult. The short-distance communication M2M card can be applied to the M2M service as follows. The short-distance communication M2M card can be installed on various terminals such as monitoring, measurement, data acquisition, etc. As the data node acquires the required state parameters and other data, each short-distance communication M2M card is organized into a network according to a certain structure, and the acquired state is obtained. The parameters are aggregated to the specified node, and sent to the management system by the designated node through the mobile network to realize remote collection and management of device data in the network. The solution includes two parts: a local wireless network and a remote mobile network. The acquired data can be transmitted and interacted in two types of networks through short-range communication M2M cards. The basic requirements of the program are as follows. 1) The local wireless network includes a management device data node and a managed device data node, wherein the managed device data node is located in the managed device, acquires state parameters of the managed device, and collects the management device through the self-organizing network; The data node is located in the management device, and collects all the managed device data node state parameters in the network and sends them to the remote management system. 2) Depending on the network organization structure, the local wireless network can have two networking modes. 1 single point system. In this way, each management network has one and only one managed device data node, which constitutes a single-point network, and the management device communicates with the unique data node in the network to obtain device state parameters; 2 multi-point system. In this manner, each management network has multiple data nodes of the managed device, and constitutes an ad hoc network. The management device acts as a unique aggregation node, and communicates with multiple managed device data nodes to acquire multiple device state parameters. The management device and the managed device form a network topology such as a star, a tree, or a mesh. According to the IEEE 802.15.4/Zigbee standard [6], the management device is a full-featured device FFD, and the managed device is a full-featured device FFD or a reduced-function device RFD. Compared with RFD, FFD is more complete in hardware function and can communicate with all other FFD or RFD. It has controller function and can provide bidirectional transmission of information. RFD can only communicate with its associated FFD and can only send. Information is received to or received from the associated FFD. 3) In addition to the local network, the short-range communication M2M card is also connected to the remote management system through the mobile network. Typically supported for this type of connection is the management device data node, which sends the aggregated device status parameters within the network to the remote management system, enabling the connection of the local wireless network to the remote mobile network. The connection between the aggregation node and the remote management system avoids the network burden caused by multiple interactions between devices caused by the direct connection between the nodes and the remote management system. 4) The remote system also includes the M2M card application management system. After the short-distance communication M2M card is connected to the system, the card application can be downloaded and updated through the over-the-air data transmission mode of the mobile network, and the data on the short-distance communication M2M card can be completed. Applications such as collections are changed, upgraded, and loaded according to business needs to implement remote management of card applications. Both the management device data node and the managed device data node can be connected to the M2M card application management system. The above implementation scheme based on short-distance communication M2M card can be widely used in business applications of electric power, transportation, industrial manufacturing, agriculture, environmental protection and other industries. 5 Summary The rapid development of M2M not only brings important impact to smart cards, but also expands new business areas and provides rare opportunities for development. Really grasp the opportunity to make the smart card break through the basic authentication function and obtain continuous development momentum. The key factor is whether it can find the M2M card business that suits the user's needs. After years of evolution, the basic capabilities of smart card technology have been significantly improved, and the achievable functions have gradually increased. In M2M, these capabilities and functions should also be fully utilized to develop the M2M card into another service bearer in the terminal device, making the M2M card service an integral part of the M2M service and expanding the scope of the M2M service. The innovation of smart card business realizes mutual promotion and common development of M2M business and smart card business, creating more significant benefits. Bags,High Quality Bags,Bags Details, CN Dongguan Yoteng Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ytpropackage.com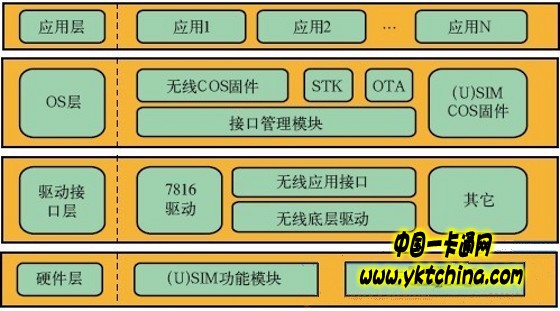
Research and Application of M2M Smart Card Technology